Mushrooms Biochar Native plant Research
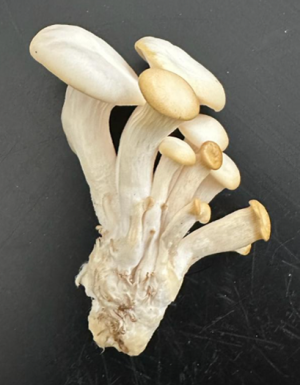
To date, food security is considered a big challenge for human population. With this regard, mushroom cultivation could be one of the alternative ways to cope with food shortage. Mushrooms play significant role for the ecosystem, environment, and human health. Considering the function play by mushrooms in the ecosystem, these latter are involved in the nutrients cycling, and they help plant up taking nutrient and water through symbiotic relationship. With respect to human health, mushrooms are loaded with important nutrients and vitamins that positively affect the healthiness of the body. In general, chemical analyses of mushrooms demonstrated great contents in vitamins A, C, and B. In addition, minerals analyses proved that edible mushrooms contents important minerals such as calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorous, potassium, copper, selenium, sodium, and zinc. Furthermore, chemical analyses of edible mushrooms revealed great contents in protein, and carbohydrates. The cultivation of edible mushrooms is significantly affected by environmental conditions and the type of substrate. Accordingly, the cultivation of these latter is generally limited in the arid and semi-arid regions where climatic conditions are the main environmental issues. Therefore, the implementations of mushrooms in such climatic milieus need additional costs that will be used either to import the different ingredients to make the substrates and or to build humidify systems. Accordingly, integrating local products with higher abundancies in the preparation of the substrates for mushrooms can allow to minimize those costs. United Arab Emirate (UAE) is considered one of the pioneers in the cultivation of date palms and dates trading. The cultivation of this plant species within the country generates significant wastes that could therefore be used to prepare substrates locally. Therefore, this project attempts to see how local products including dates palms leaves, biochar and rockwool and any other material, which is fully available locally could be used to prepare the mushroom substrate in Fujairah. To experiment this, then we selected around 10 local products that we used to prepare the substates of the Oyster mushrooms. Our recent findings in the cultivation of this species of edible mushrooms demonstrated that many local products can be used to grow Oyster mushrooms in the Emirate of Fujairah. Low nutrients availability is considered one of the major issues that greatly affect crops production and afforestation Projects in the arid and semi-arid regions. In the past centuries, farms used significant amounts of chemical fertilizers to improve crop production while implementing their farms. Recent findings demonstrated that, such levels of chemical fertilizers application adversely alter the soil quality, and environmental conditions. In this regard, biochar is seen as the alternative way to improve the soil quality and agricultural systems. Biochar not only helps in the soil and plant quality improvement but also, it helps in the process of carbon sequestration, decreasing of greenhouse gas emissions, and nutrients dynamics. More recently, soil-biochar application showed important role in improving soil biological activities plant or crops resistance to abiotic and biotics factors. Therefore, researchers of the Fujairah Research Centre are currently working on the biochar establishment integrating dates palm leaves. Our recent results indicated that dates palm trees parts are a good source for biochar preparation the Emirate of Fujairah. We observed important variations in the chemical composition of the tested biochar. With the main goal to control the desertification process and to stabilize soil against natural erosion then, Prosopis juliflora plants commonly called mesquite were introduced in the UAE but unfortunately, those have escaped cultivation areas and invaded many pastoral lands. The invasion of this plant not only affect the biodiversity, but it also negatively alters soil quality, water table, animal, and human health. Therefore, many earlier works have tried to suggested control methods to mitigate the side negative effects of mesquite plants without success. Therefore, and with the main objective to find out utilizable ways related the mesquite plants, then we explored its chemical composition and we associated this with the antimicrobial activities. Our findings revealed that P. juliflora plants are a good source of nutrients, the plant chemical composition revealed that mesquite plant parts could be used to fight against some virulent pathogens related to human health.
